Need help with Green Hydrogen? This Guide is Your Answer!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Green Hydrogen, where we unravel the mysteries surrounding this revolutionary clean fuel source.
Green hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution in a world increasingly focused on sustainability and combating climate change.
From its production to its potential applications, understanding green hydrogen is essential for anyone interested in shaping a greener future.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Green Hydrogen, where we unravel the mysteries surrounding this revolutionary clean fuel source.
Green hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution in a world increasingly focused on sustainability and combating climate change.
From its production to its potential applications, understanding green hydrogen is essential for anyone interested in shaping a greener future.
What is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen represents a pivotal step towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape. But what exactly is green hydrogen, and why is it garnering so much attention?
Simply put, green hydrogen is produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources such as wind or solar.
Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods, which often rely on fossil fuels and emit harmful greenhouse gases, green hydrogen production generates zero emissions. This makes it a key player in the transition to a carbon-neutral economy.
Simply put, green hydrogen is produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources such as wind or solar.
Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods, which often rely on fossil fuels and emit harmful greenhouse gases, green hydrogen production generates zero emissions. This makes it a key player in the transition to a carbon-neutral economy.
Understanding Green Hydrogen Production
To comprehend the significance of green hydrogen, it's imperative to grasp the intricacies of its production process.
Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods green hydrogen is derived from renewable sources through electrolysis.
Electrolysis involves splitting water molecules (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using an electrical current. This process requires two electrodes immersed in water, typically separated by a membrane, to prevent the gases from recombining.
When an electric current is applied, water molecules at the cathode (negative electrode) gain electrons and form hydrogen gas, while oxygen gas is produced at the anode (positive electrode).
What sets green hydrogen apart is the source of electricity used in the electrolysis process. Instead of relying on fossil fuels, green hydrogen production utilises renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower.
The entire production chain becomes emissions-free by harnessing these clean energy sources, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods green hydrogen is derived from renewable sources through electrolysis.
Electrolysis involves splitting water molecules (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using an electrical current. This process requires two electrodes immersed in water, typically separated by a membrane, to prevent the gases from recombining.
When an electric current is applied, water molecules at the cathode (negative electrode) gain electrons and form hydrogen gas, while oxygen gas is produced at the anode (positive electrode).
What sets green hydrogen apart is the source of electricity used in the electrolysis process. Instead of relying on fossil fuels, green hydrogen production utilises renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower.
The entire production chain becomes emissions-free by harnessing these clean energy sources, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
Why Does Green Hydrogen Matter?
Green hydrogen must balance addressing climate change and achieving sustainability goals. As the world seeks alternatives to fossil fuels, green hydrogen offers a versatile and scalable solution across various sectors.
One of the primary reasons green hydrogen matters is its potential to decarbonise industries with high emissions, such as transportation, manufacturing, and heating. By replacing fossil fuels with hydrogen, these industries can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Moreover, green hydrogen is critical to unlocking the full potential of renewable energy sources. Solar and wind power, while abundant, are intermittent and dependent on weather conditions. By converting excess renewable energy into hydrogen through electrolysis, we can store and transport energy more efficiently, ensuring a reliable supply of clean energy even when the sun isn't shining or the wind isn't blowing.
In addition to its environmental benefits, green hydrogen also presents economic opportunities, driving innovation, job creation, and investment in renewable energy infrastructure. Countries and companies leading the way in green hydrogen technology stand to gain a competitive edge in transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
One of the primary reasons green hydrogen matters is its potential to decarbonise industries with high emissions, such as transportation, manufacturing, and heating. By replacing fossil fuels with hydrogen, these industries can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Moreover, green hydrogen is critical to unlocking the full potential of renewable energy sources. Solar and wind power, while abundant, are intermittent and dependent on weather conditions. By converting excess renewable energy into hydrogen through electrolysis, we can store and transport energy more efficiently, ensuring a reliable supply of clean energy even when the sun isn't shining or the wind isn't blowing.
In addition to its environmental benefits, green hydrogen also presents economic opportunities, driving innovation, job creation, and investment in renewable energy infrastructure. Countries and companies leading the way in green hydrogen technology stand to gain a competitive edge in transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
Exploring Green Hydrogen Technology
Delving into the technology behind green hydrogen production unveils a landscape of innovation and potential. Various methods and technologies are being developed and deployed to optimise green hydrogen production's efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
One key component of green hydrogen technology is the electrolyser. Electrolysers come in different types, including alkaline, polymer electrolyte membranes (PEM), and solid oxide electrolysers.
Each type has advantages and limitations, influencing efficiency, operating temperature, and scalability.
Alkaline electrolysers, for instance, are known for their simplicity and reliability.
In addition to electrolyser technology, advancements in renewable energy integration, hydrogen storage, and distribution infrastructure are critical for the widespread adoption of green hydrogen.
One key component of green hydrogen technology is the electrolyser. Electrolysers come in different types, including alkaline, polymer electrolyte membranes (PEM), and solid oxide electrolysers.
Each type has advantages and limitations, influencing efficiency, operating temperature, and scalability.
Alkaline electrolysers, for instance, are known for their simplicity and reliability.
In addition to electrolyser technology, advancements in renewable energy integration, hydrogen storage, and distribution infrastructure are critical for the widespread adoption of green hydrogen.
The Role of Green Hydrogen in Combatting Climate Change
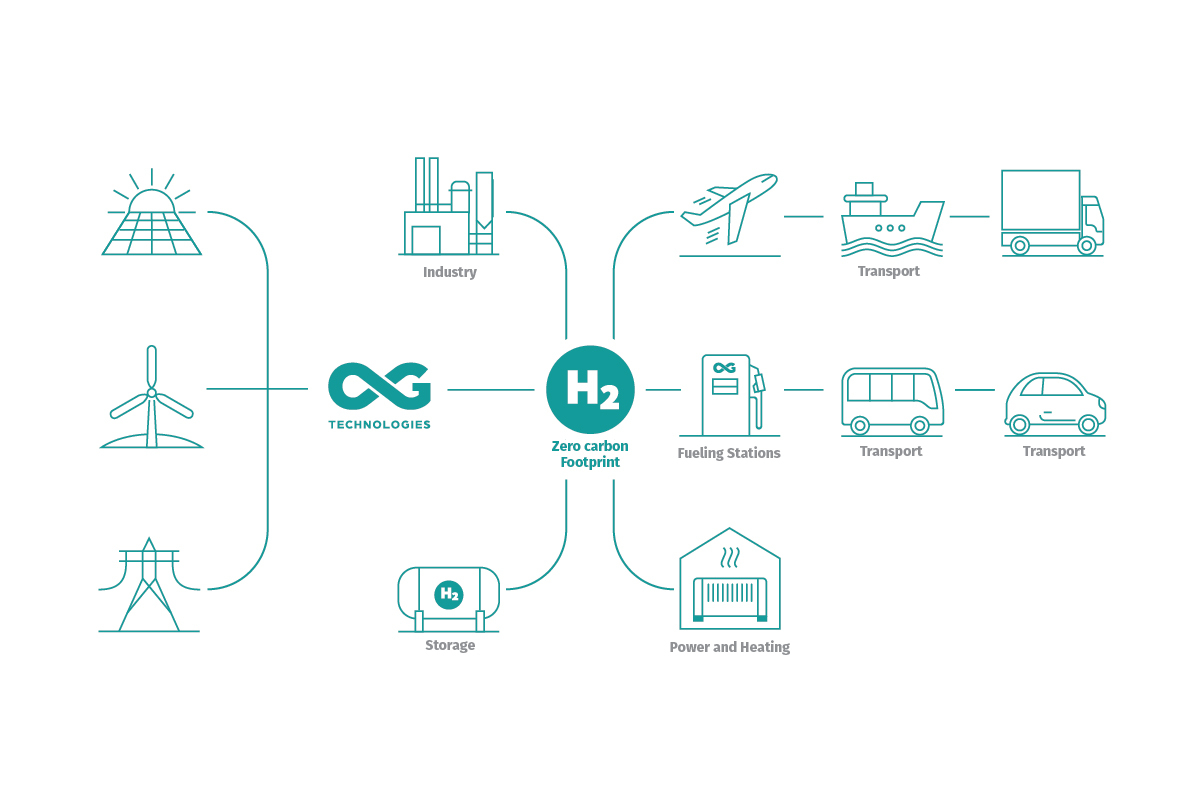
At the heart of the green hydrogen revolution lies its potential to combat climate change and accelerate the transition to a low-carbon future. By replacing fossil fuels in crucial sectors such as transportation, industry, and power generation, green hydrogen can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help limit global warming.
Transportation represents a particularly promising avenue for green hydrogen deployment. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) powered by hydrogen offer zero-emission mobility with fast refuelling times and extended driving ranges, overcoming some of the limitations of battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
Moreover, hydrogen fuel cells can be integrated into various modes of transportation, including cars, trucks, buses, trains, ships, and even aircraft, offering a versatile solution for decarbonising the transportation sector.
In the industrial sector, green hydrogen can replace fossil fuels as a feedstock for processes such as ammonia production, steelmaking, and petrochemical refining, reducing emissions from these traditionally carbon-intensive industries.
In power generation, green hydrogen holds the potential to complement renewable energy sources by providing energy storage and grid-balancing capabilities.
By storing excess renewable energy as hydrogen during periods of low demand and converting it back to electricity via fuel cells or combustion turbines during peak demand, green hydrogen can help stabilise the grid and facilitate the integration of intermittent renewables.
As nations and industries strive to meet their climate targets and transition to a sustainable energy future, the role of green hydrogen as a versatile, scalable, and emissions-free energy carrier cannot be overstated.
By embracing green hydrogen technologies and fostering collaboration between governments, industries, and stakeholders, we can unlock the full potential of this clean fuel and pave the way for a brighter, greener tomorrow.
Transportation represents a particularly promising avenue for green hydrogen deployment. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) powered by hydrogen offer zero-emission mobility with fast refuelling times and extended driving ranges, overcoming some of the limitations of battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
Moreover, hydrogen fuel cells can be integrated into various modes of transportation, including cars, trucks, buses, trains, ships, and even aircraft, offering a versatile solution for decarbonising the transportation sector.
In the industrial sector, green hydrogen can replace fossil fuels as a feedstock for processes such as ammonia production, steelmaking, and petrochemical refining, reducing emissions from these traditionally carbon-intensive industries.
In power generation, green hydrogen holds the potential to complement renewable energy sources by providing energy storage and grid-balancing capabilities.
By storing excess renewable energy as hydrogen during periods of low demand and converting it back to electricity via fuel cells or combustion turbines during peak demand, green hydrogen can help stabilise the grid and facilitate the integration of intermittent renewables.
As nations and industries strive to meet their climate targets and transition to a sustainable energy future, the role of green hydrogen as a versatile, scalable, and emissions-free energy carrier cannot be overstated.
By embracing green hydrogen technologies and fostering collaboration between governments, industries, and stakeholders, we can unlock the full potential of this clean fuel and pave the way for a brighter, greener tomorrow.
Overcoming Challenges and Scaling Up
While the potential of green hydrogen is undeniable, several challenges must be addressed to realise its widespread adoption and scale-up.
Infrastructure development is a critical challenge facing the scaling up of green hydrogen.
Building the necessary hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and distribution infrastructure requires significant investment and coordination among governments, industries, and stakeholders.
This includes establishing hydrogen refuelling stations for fuel cell vehicles, retrofitting existing industrial facilities for hydrogen use, and constructing pipelines or shipping terminals for hydrogen transport.
Moreover, ensuring the sustainability of green hydrogen production is essential to its long-term viability. While green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, its environmental footprint can vary depending on factors such as the source of renewable energy, the efficiency of electrolysis technology, and the use of water resources.
Minimising environmental impacts and promoting responsible production practices are crucial for maximising the ecological benefits of green hydrogen.
Policy support and regulatory frameworks play a critical role in overcoming these challenges and accelerating the adoption of green hydrogen.
Governments worldwide increasingly recognise the potential of green hydrogen and implement policies to incentivise its production, deployment, and research.
These policies include renewable energy targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, investment incentives, and hydrogen-specific regulations.
International collaboration and knowledge sharing are vital for advancing green hydrogen technology and addressing global energy challenges.
By leveraging expertise, resources, and best practices from across the globe, we can accelerate innovation, drive down costs, and overcome barriers to deployment.
Infrastructure development is a critical challenge facing the scaling up of green hydrogen.
Building the necessary hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and distribution infrastructure requires significant investment and coordination among governments, industries, and stakeholders.
This includes establishing hydrogen refuelling stations for fuel cell vehicles, retrofitting existing industrial facilities for hydrogen use, and constructing pipelines or shipping terminals for hydrogen transport.
Moreover, ensuring the sustainability of green hydrogen production is essential to its long-term viability. While green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, its environmental footprint can vary depending on factors such as the source of renewable energy, the efficiency of electrolysis technology, and the use of water resources.
Minimising environmental impacts and promoting responsible production practices are crucial for maximising the ecological benefits of green hydrogen.
Policy support and regulatory frameworks play a critical role in overcoming these challenges and accelerating the adoption of green hydrogen.
Governments worldwide increasingly recognise the potential of green hydrogen and implement policies to incentivise its production, deployment, and research.
These policies include renewable energy targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, investment incentives, and hydrogen-specific regulations.
International collaboration and knowledge sharing are vital for advancing green hydrogen technology and addressing global energy challenges.
By leveraging expertise, resources, and best practices from across the globe, we can accelerate innovation, drive down costs, and overcome barriers to deployment.
Looking Ahead
Green hydrogen's potential to revolutionise the energy landscape and drive sustainable development is immense as we look to the future. Green hydrogen offers a versatile and scalable solution to the world's energy needs, from powering transportation and industry to stabilising the grid and supporting renewable energy integration.
However, realising this potential requires concerted efforts and collaboration among governments, industries, academia, and civil society. It requires bold investments in research and development, ambitious policy measures to incentivise green hydrogen deployment, and a commitment to sustainability and environmental stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions
However, realising this potential requires concerted efforts and collaboration among governments, industries, academia, and civil society. It requires bold investments in research and development, ambitious policy measures to incentivise green hydrogen deployment, and a commitment to sustainability and environmental stewardship.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is green hydrogen the same as blue hydrogen? While green and blue hydrogen aim to reduce carbon emissions, they differ in their production methods. Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, while blue hydrogen is derived from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology to mitigate emissions.
- How efficient is electrolysis for green hydrogen production? Electrolysis efficiency varies depending on factors such as the type of electrolyser, the purity of the hydrogen produced, and the source of electricity. Advances in electrolysis technology continue to improve efficiency and reduce costs, making green hydrogen more competitive with conventional fuels.
- What are the main challenges facing the widespread adoption of green hydrogen? Despite its potential, green hydrogen faces challenges related to cost competitiveness, infrastructure development, and scaling up production. Addressing these challenges will require concerted efforts from governments, industries, and researchers to drive innovation and investment in green hydrogen technologies.
- What are the potential applications of green hydrogen beyond transportation and industry? In addition to transportation and industry, green hydrogen has potential applications in sectors such as power generation, heating, and energy storage. Furthermore, hydrogen energy storage systems can help balance renewable energy grids and provide backup power during periods of high demand.
- How can businesses and industries benefit from integrating green hydrogen into their operations? Incorporating green hydrogen into business operations can offer various benefits, including reduced carbon emissions, enhanced energy security, and increased resilience to energy market fluctuations. By transitioning to green hydrogen, industries can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability, meet regulatory requirements, and gain a competitive edge in the growing market for clean energy solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, green hydrogen represents a transformative solution to the dual challenges of climate change and energy security.
From production to applications, green hydrogen offers a pathway to a cleaner, more sustainable future for future generations. By harnessing the power of renewable energy and innovative technologies, we can turn the promise of green hydrogen into reality and build a world powered by clean, abundant, and accessible energy sources.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of green hydrogen. Let's make the promise of clean, abundant hydrogen a reality together.
Ready to learn more about green hydrogen and its transformative potential?
Contact Hydrogenera today to explore how you can be part of the clean fuel revolution.
From production to applications, green hydrogen offers a pathway to a cleaner, more sustainable future for future generations. By harnessing the power of renewable energy and innovative technologies, we can turn the promise of green hydrogen into reality and build a world powered by clean, abundant, and accessible energy sources.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of green hydrogen. Let's make the promise of clean, abundant hydrogen a reality together.
Ready to learn more about green hydrogen and its transformative potential?
Contact Hydrogenera today to explore how you can be part of the clean fuel revolution.